GitlabCI
You can integrate driftctl in GitlabCI by taking as example this repository.
You can integrate driftctl within your GitOps workflow to get something like this:
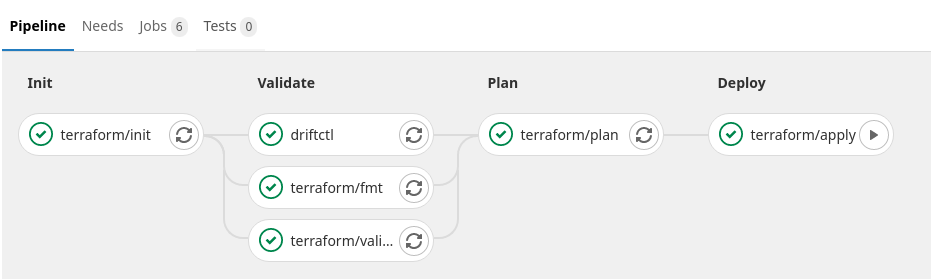
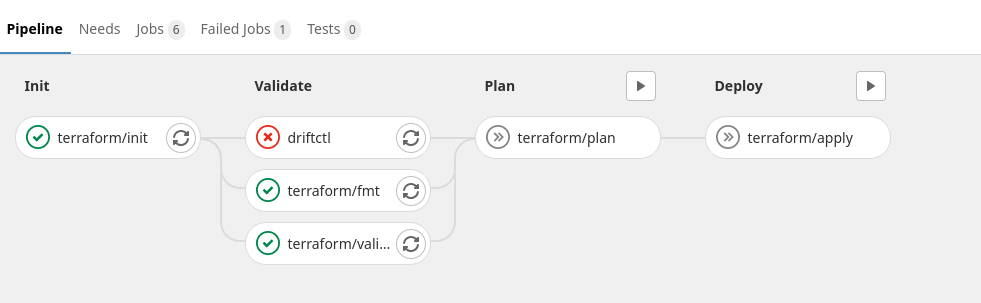
In this kind of workflow if a new drift happens it will block your pipeline execution:
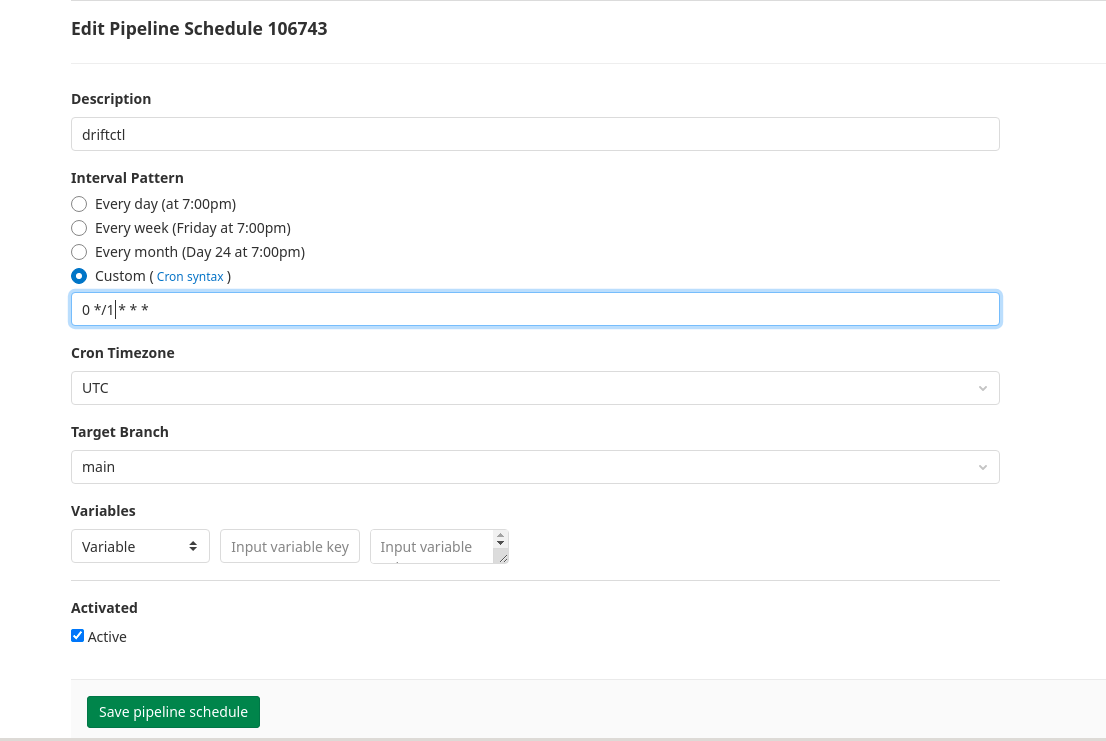
You can also setup a scheduled job to detect drifts as they happen, in the screenshot below it schedules a driftctl run every hour
Full example
Below you can find a full GitlabCI example with a complete GitOps workflow example and a scheduled run of driftctl.
stages:
- init
- validate
- plan
- deploy
.driftctl:
image:
name: snyk/driftctl
entrypoint: [""]
script:
- driftctl scan
# ====================
# Scheduled driftctl run
# ====================
# Scheduled driftctl run
driftctl:scheduled:
extends: .driftctl
only:
- schedules
stage: validate
variables:
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION: us-east-1
DCTL_FILTER: "Type=='aws_s3_bucket'"
# ====================
# Classic GitOps workflow
# ====================
# Used to share .terraform cached providers in terraform jobs
.tfcache: &tfcache
cache:
key: ${CI_PIPELINE_ID}
paths:
- .terraform
# Terraform image to use for every terraform jobs
.terraform: &terraform
image:
name: hashicorp/terraform:0.14.4
entrypoint: [""]
terraform/init:
<<: *terraform
<<: *tfcache
stage: init
except:
- schedules
script:
- terraform init
driftctl:
extends: .driftctl
except:
- schedules
stage: validate
variables:
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION: us-east-1
DCTL_FILTER: "Type=='aws_s3_bucket'"
terraform/fmt:
<<: *terraform
stage: validate
except:
- schedules
script:
- terraform fmt -check -diff
terraform/validate:
<<: *terraform
<<: *tfcache
stage: validate
except:
- schedules
script:
- terraform validate
terraform/plan:
<<: *terraform
<<: *tfcache
stage: plan
except:
- schedules
artifacts:
name: plan
expire_in: 1 day
paths:
- "plan.out"
script:
- terraform plan -out=plan.out
terraform/apply:
<<: *terraform
<<: *tfcache
stage: deploy
when: manual
dependencies:
- terraform/plan
except:
- schedules
script:
- terraform apply plan.out